
This paper compares the nutrient profile of soybean meal (SBM) samples from the USA and Brazil. Proximate analysis, total amino acids, standardized ileal digestibility (SID) of amino acids, apparent metabolizable energy (AME), and phytic phosphorus were estimated using near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) with calibrations derived from chemical analyses and in vivo determinations. The study found nutritional profiles of both SBM origins to be similar. A significant difference was observed in AME content in favour of US meal (9.59 ± 0.075 MJ/kg vs. 9.38 ± 0.084 MJ/kg, P < 0.05), whereas SBM from Brazil contained slightly higher level of digestible lysine (25.4 vs. 24.6 g/kg, P > 0.05). In addition, US meals displayed lower variation in terms of crude protein, AME, crude fibre etc.
Introduction
Soybean meal is the most widely used protein source in poultry diets, because of its high levels of crude protein, high digestibility and consistency compared to other protein ingredients. However, its nutritional value is affected by several factors, such as genetic selection, production or planting environment and crushing process, which affect the concentration of both nutrients and anti-nutritional factors (ANF). There are numerous studies on the quality and consistency of SBM. Some authors compared quality of soybeans and soybean meals from US and other origins; others reported soybeans from China contained a higher crude protein and a lower lipid level than those from Brazil. Other authors reported soybean meals produced in Argentina and Brazil have lower true TAA digestibility than US SBM and still others reported crushing procedures and conditions affect nutritional value.
Today, US and Brazil are the two dominant sources in terms of soybean production and exportation. The livestock industry has a keen interest in quantifying the variation of soybean and soybean meals. The objective of this study was to survey the quality of SBM from the US and Brazil, especially for their metabolisable energy and SID amino acids which have not been well defined due to complexity in determination.
Materials and methods
In this study, to eliminate differences derived from processing conditions, raw soybeans were imported directly from US and Brazil, crushed and produced by the same SBM manufacturer in Vietnam. Imported soybeans were crushed within 10 days. Five samples from each origin were randomly collected during each day’s crushing. Consequently, a total of 100 SBM samples was obtained, in which 50 samples originated from US and the rest 50 from Brazil. Nutritional values including proximate analysis, total amino acids, standardized ileal digestibility of amino acid and apparent metabolizable energy (AME) values were evaluated using Adisseo’s near infrared reflectance spectroscopy (NIRS) predictive equations derived from in vivo digestibility tests. In parallel, the SBM samples were analysed for the contents of proximate nutrients by a third party laboratory in Vietnam.
NIRS prediction for nutria contents in SBM
Feasibility of using NIRS to predict nutrition content has been proven by previous studies. Adisseo Precise Nutrition Evaluation (PNE) services integrated both in vivo expertise and NIRS technology to offer on-line NIR platform since 2012. Available parameters include AME, total and standardized ileal digestible amino acids, total, phytic and available phosphorous for poultry and pigs, and proximate nutrients. Digestibility coefficients were determined in vivo, using the model of adult caecectomized ISA Brown cockerels, with caeca surgically removed in order to minimise intestinal microflora interference. A Precise Nutrition Evaluation (PNE) AME database was obtained through in vivo measurements using 3-week-old male broilers, following the European reference method with ad libitum feeding and total excreta collection.
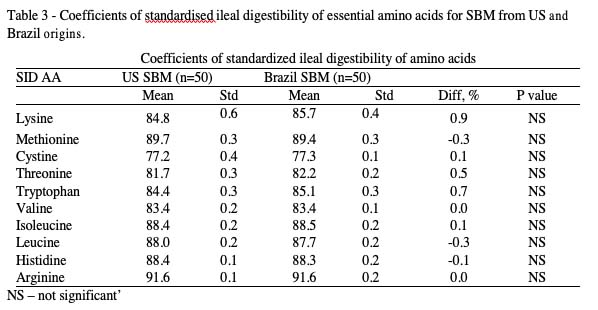
The proximate nutrients of SBM samples were determined by both NIRS and laboratory as shown in Table 1. Consistent results obtained by NIRS and laboratory tests demonstrate the reliability of using NIRS to predict the nutritional values. As the dry matter content of samples was similar, nutrient values on a dry matter basis were not calculated. The proximate compositions are similar for SBM from US and Brazil origins, except for protein content which is slightly higher for Brazil SBM (467.7 g/kg, as fed) compared to US SBM (460.7 g/kg, as fed), but with no statistical difference (P > 0.05). In addition, total phosphorus and phytic phosphorus have been found similar when comparing SBM from US and Brazil.
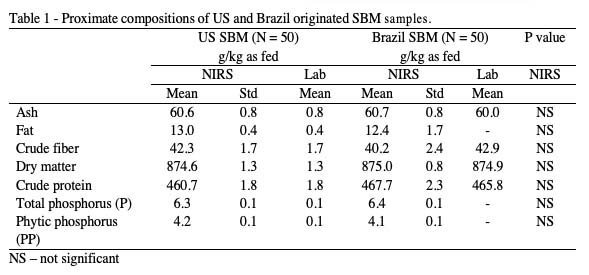
The concentrations of essential amino acids of SBM from US and Brazil origins were found to be similar and consistent (Table 2), particularly when the amino acids concentrations were expressed in percentage of crude protein. The concentration differences ranged between -0.04 to 0.11 (in % of crude protein), with no statistical difference (P > 0.05).
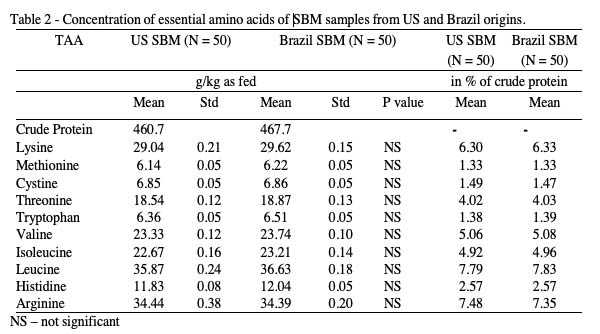
Coefficients for SID of amino acids reflected similar values when comparing US SBM and Brazil SBM (Table 3). Lysine digestibilities were found at 84.8 % and 85.7 % for US SBM and Brazil SBM respectively, which is in line with common reference and methionine digestibilities were 89.7 % and 89.4 % for US SBM and Brazil, respectively. Similar AA digestibilities may be due to the same processing conditions used in this study since the digestibility of AA is influenced largely by the adequacy of heat-processing to destroy or reduce the ANF, especially trypsin inhibitors.
Besides AA digestibility, metabolizable energy has a high impact on animal performance and consequently on profitability. Significant differences were observed in the apparent metabolizable energy (AME) related to soybean origin: Average AME 9.59 MJ/kg for US SBM vs. 9.39 MJ/kg for Brazil SBM (P<0.05). Similarly, nitrogen corrected AME (AMEn) for US SBM was 8.83 MJ/kg (Figure 1), higher than Brazil SBM at 8.59 MJ/kg (P<0.05).
In addition, US SBM had higher consistency for most of the nutrient contents compared with Brazil SBM. Except for dry matter content, smaller standard deviation values were observed for US SBM (1.80 g/kg for CP and 0.075 MJ/kg for AME), compared to Brazil SBM (2.25 g/kg for CP and 0.084 MJ/kg for AME). The low variability in the US samples is probably due to the low genetic variability among current US soybean cultivars.
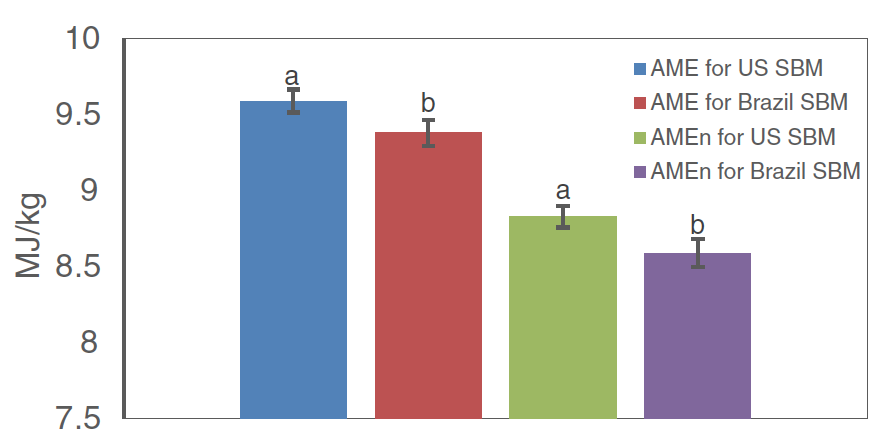
a and b values with different superscripts are significantly (P < 0.05) different from each other.
Conclusions
The NIRS technique has unique advantages of being non-destructive and rapid in screening the quality of any given feed ingredient. Predicting from the in vivo referenced NIRS calibrations, this study demonstrated that soybean meal from US origin has higher AME and AMEn values than soybean meal from Brazil. Overall, US originated soybean meal also showed better consistency for most nutrients with smaller standard deviation values, which highlighted the potential economic benefit of SBM from the US.
References are available on request.
From the Proceedings of the Australian Poultry Science Symposium 2019.

















