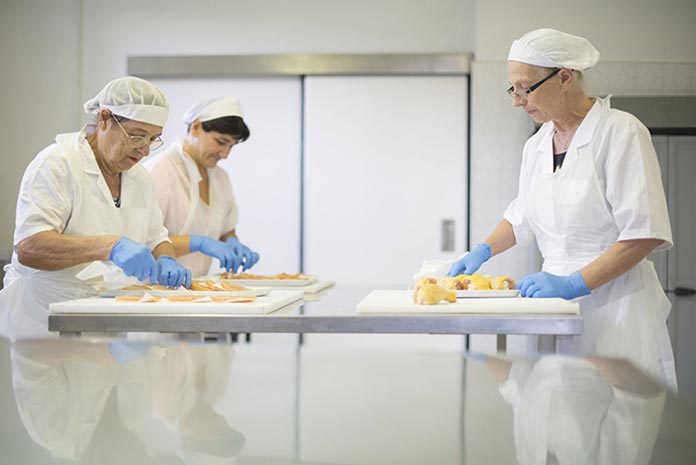
Poultry meat is a source of cheap and healthy protein, which is the recipe for success in the world of growing meat consumption of more than 300 million tons. The growing population and the growing spending income globally especially in societies with a relatively low average spending income, create a multiplier effect for the demand of meat. Today food business operators are challenged to meet the demands of citizens and consumers in a globalized world. These demands pertain to different domains as food safety, animal health and welfare, environment and fair practices. As the interests in these fields may be conflicting, it is the food business operators responsibility to balance them in a sustainable way.
Food safety
The European Union has authorized the specific use of a number of chemical substances as feed and food additives, colors and flavorings and antimicrobials in the production of poultry meat. However, the use of hormonal substances for growth promotion in farm animals is prohibited. Apart from the intentional use of chemical substances, a number of them are present in the environment and might be unintentionally contaminate the animals and their products by the raw materials used in the production or by the system of production. To safeguard consumers official controls in the feed and food chain have regularly made to check the absence of prohibited substances as hormones and the compliance of poultry with the set maximum residue level for a number of contaminants, such as mycotoxins, metals, dioxins and PCB’s, pesticides and veterinary medicines. The biological hazards from poultry are mostly concentrating on the pathogens Salmonella and Campylobacter. To fight against Campylobacter a number of Member States have introduced action plans setting a reduction target for the number of Campylobacter on poultry carcasses. Antimicrobial resistance is another issue that may negatively impact on the bacterial susceptibility for critically important antibiotics used for effective treatment of Salmonella and Campylobacter infections in humans. Strict biosecurity protocols on the farm and a strong food hygiene practice in the slaughterhouse including robust sampling and testing plans will be needed to control better the biological hazards in the poultry chain.
Poultry health and welfare
Keeping poultry healthy is the basic for the birds’ welfare. Healthy animals are more productive than sick animals. Therefore, poultry farmers and poultry meat producers have an interest in prevention of diseases by biosecurity including vaccination. These are also the key elements in the European health strategy and policy. In addition after an outbreak of a contagious disease, regionalization and zoning together with culling, are the main actions to get the disease under control and eradicated. The European legislation imposes many obligations that must protect the animals during their stay on the farm, during transport and at the time of slaughter or killing. The Welfare Quality Project defines the European standards for on-farm welfare assessment and product information systems, as well as practical strategies for improving animal welfare. Welfare indicators are used by operators to establish the welfare situation of poultry and take corrective actions if needed. Private standard schemes may define welfare criteria beyond the ones in legislation.
Environment
Efficient use of resources in food production and reducing wastage during production and consumption of food are determining the level of environmental sustainability in the poultry chain.
Apart from the initiatives in the EU there is the multi-stakeholder initiative ‘Partnership on the environmental benchmarking of livestock supply chains’ (LEAP) with the FAO’s Animal Production and Health Division and a group of agriculture and food business representatives.
It is essential that the business operators demonstrate towards the society they are trustworthy by being accountable and transparent about using sustainable processes and techniques. Consequently, this will create a better perception and image of poultry meat with consumers and keeping their confidence in poultry meat. Finally, it will give the poultry sector a strong license to produce.